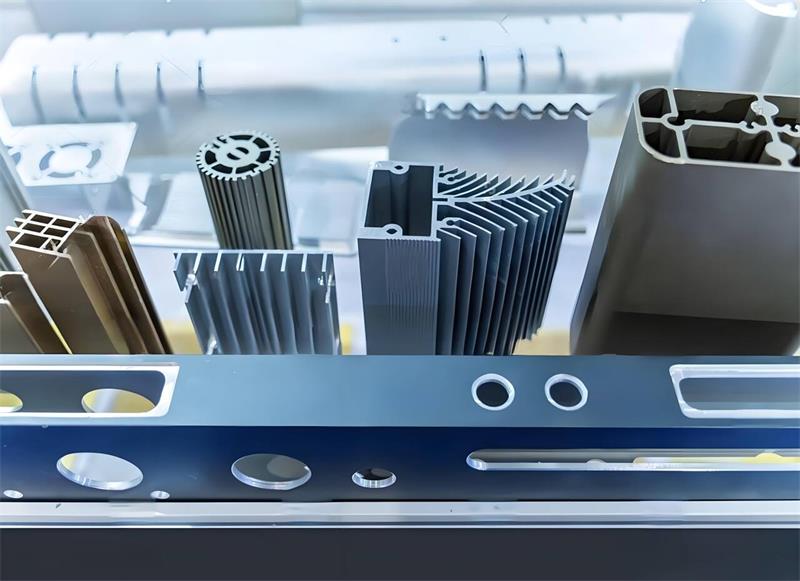
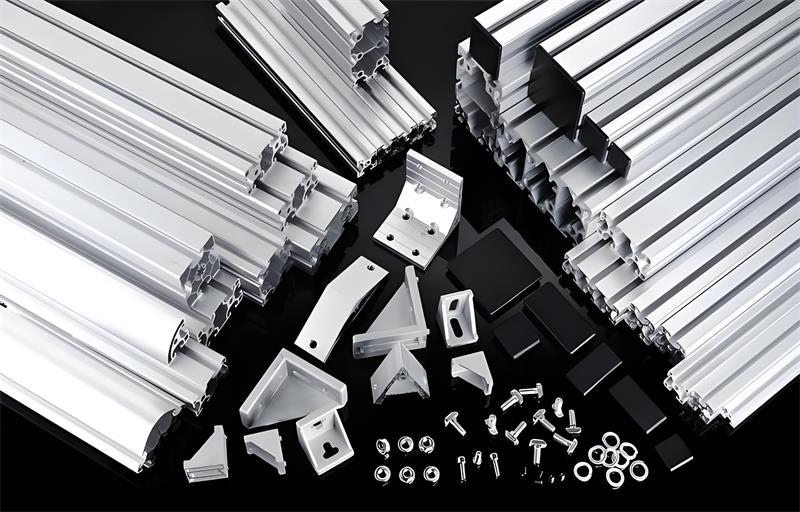
Where are aluminium profiles used
OUTLINE
I. Introduction
Highlight the significance of aluminum profiles in modern life and introduce the exploration of their wide applications.
II. Basics of Aluminium Extrusion Profiles
Definition: Explain the process of forming specific cross-sectional shapes by extruding heated aluminum through a die.
Extrusion Process: Describe heating the billet, applying pressure, and the advantage of high precision.
III. Applications in Various Industries
Construction: Discuss uses in windows, doors, curtain walls, roofing, and supports.
Automotive: Detail applications in body frames, trims, and engine components.
Industrial: Explain in frames and conveyor systems.
Marine: Mention in boat hulls, decks, and docks.
Aerospace: Highlight in aircraft structures and interiors.
IV. Conclusion
Summarize the indispensability and pose an innovative application question
I. Introduction
In today's modern world, aluminum profiles have become an integral part of our daily lives, playing a crucial role in various industries. From the sleek frames of our office windows to the intricate structures of high-speed trains, these versatile components made from aluminum are everywhere. But have you ever stopped to wonder just how widespread their applications are? In this blog post, we'll take a fascinating journey through different sectors to uncover the many places where aluminum profiles are used and why they have become the material of choice for so many applications. Whether you're a construction enthusiast, a manufacturing professional, or simply curious about the materials that shape our world, join us as we explore the diverse uses of aluminum profiles.
II. What Are Aluminium Extrusion Profiles?
A. Defining Aluminium Extrusion Profiles
Aluminium extrusion profiles are structural components that are formed by forcing heated aluminium through a die. This process gives the aluminium a specific cross-sectional shape, which can range from simple geometric forms like squares, rectangles, and circles to highly complex and custom designs. Essentially, it's like squeezing toothpaste out of a tube, but instead of toothpaste, it's molten aluminum, and the tube is a precisely engineered die that imparts the desired shape to the metal. The resulting profiles are the building blocks for countless applications, thanks to their versatility, strength, and lightweight nature.
B. The Extrusion Process
The extrusion process is a marvel of modern manufacturing. It begins with heating the aluminium billet to a specific temperature range, typically between 400 to 500 degrees Celsius, depending on the alloy. This makes the aluminium soft and malleable, ready to be shaped. The heated billet is then placed in the extrusion press, and hydraulic pressure is applied to push it through the die. As the aluminium passes through the die, it takes on the exact shape of the die's opening, emerging as a continuous length of the desired profile. What's remarkable is that this process allows for high precision and repeatability, enabling manufacturers to produce profiles with tight tolerances. This means that whether you need a standard rectangular profile for a window frame or a highly customized shape for a specialized industrial application, the extrusion process can deliver it while maintaining the structural integrity of the aluminium. This ability to create durable and customizable profiles is what makes aluminium extrusion so widely used across diverse industries.
III. Aluminium Profiles in Diverse Industries
A. Construction Industry
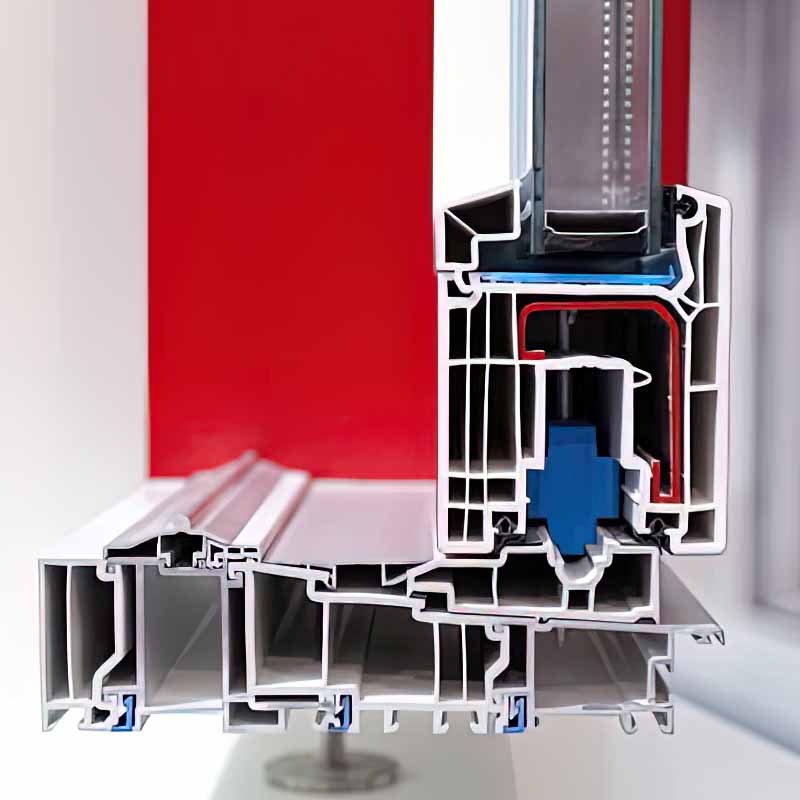
1. Aluminium Windows and Doors
One of the most common applications of aluminium profiles is in the construction of windows and doors. Aluminium's natural resistance to weathering and corrosion makes it an ideal choice for framing these openings. In residential homes, you'll often find aluminium window frames that not only provide a sleek and modern look but also offer durability and energy efficiency. Unlike some other materials, aluminium doesn't rot, warp, or swell when exposed to moisture, ensuring that your windows and doors maintain their structural integrity over time. This is especially crucial in areas with high humidity or frequent rainfall. Additionally, aluminium profiles can be easily customized to fit various architectural designs, whether you're going for a traditional casement window or a large, floor-to-ceiling sliding door. They can also support double or triple glazing, enhancing insulation and reducing heat transfer, which helps in keeping your home warm in the winter and cool in the summer.
2. Curtain Walls
In modern architecture, curtain walls have become a staple, and aluminium profiles play a central role in their construction. Curtain walls are non-structural outer coverings that adorn the facades of buildings, providing an aesthetically pleasing appearance while protecting the interior from the elements. Aluminium extrusion profiles are used to create the framework for these curtain walls, allowing for large expanses of glass or other cladding materials to be installed. The lightweight nature of aluminium is a significant advantage here, as it reduces the load on the building's structure, enabling architects to design taller and more innovative buildings. Moreover, aluminium curtain walls can be fabricated off-site and then assembled quickly, saving construction time and costs. They also offer excellent thermal and acoustic insulation, creating a comfortable indoor environment even in noisy and extreme weather conditions.
3. Roofing and Structural Supports
When it comes to roofing and structural supports in both residential and commercial construction, aluminium's strength-to-weight ratio shines. Aluminium profiles are used to fabricate beams, columns, and roofing systems that can withstand heavy loads while being relatively light. This not only simplifies the construction process but also reduces the overall weight of the building, which can have implications for foundation design and seismic resistance. For example, in industrial warehouses, aluminium roof trusses are often employed to cover large areas without the need for excessive supporting columns, maximizing interior space. In residential applications, aluminium roofing sheets and profiles are gaining popularity due to their durability, resistance to rust, and ability to reflect sunlight, helping to keep the building cooler. Overall, aluminium's versatility in construction applications makes it a go-to material for architects and builders looking to balance strength, aesthetics, and functionality.
B. Automotive Industry
1. Body Frames
The automotive industry has been on a quest for lighter materials to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, and aluminium profiles have emerged as a key solution. Aluminium is increasingly being used to construct the body frames of cars, trucks, and SUVs. By replacing traditional steel frames with aluminium ones, manufacturers can significantly reduce the vehicle's weight. This weight reduction translates into better fuel economy, allowing cars to travel further on a tank of gas. It also enhances performance, as the lighter frame enables quicker acceleration and more agile handling. For instance, high-end sports cars often utilize aluminium-intensive chassis to achieve a lower center of gravity and superior driving dynamics. Additionally, aluminium's recyclability aligns with the automotive industry's growing focus on sustainability, as recycled aluminium can be used to produce new components with minimal loss of quality.
2. Trims and Exterior Components
Aluminium profiles are not only used in the structural aspects of vehicles but also for decorative and functional trims and exterior components. From window surrounds and door handles to bumpers and side skirts, aluminium adds a touch of elegance and durability. In harsh weather conditions, such as rain, snow, and road salt, aluminium's corrosion resistance ensures that these exterior parts maintain their appearance and functionality over the vehicle's lifespan. The material can be easily shaped and finished to match the overall design theme of the car, whether it's a sleek and minimalist look or a bold and aggressive style. Powder coating or anodizing aluminium trims can further enhance their resistance to scratches and fading, keeping the vehicle looking new for longer.
3. Lightweight Engine Components
Under the hood, many automakers are turning to aluminium profiles to reduce the weight of engine components. Aluminium cylinder heads, intake manifolds, and engine blocks are becoming more prevalent. The use of aluminium in these parts not only reduces the overall weight of the engine but also improves its thermal conductivity. This means that heat can be dissipated more efficiently, leading to better engine performance and reduced risk of overheating. Lighter engine components also contribute to the vehicle's overall weight reduction, further enhancing fuel efficiency and handling. For example, in some hybrid and electric vehicles, where every ounce matters for maximizing range, aluminium engine components are crucial in achieving optimal energy consumption.
D. Industrial Applications
1. Frames and Support Systems
In industrial machinery and manufacturing, aluminium profiles are the building blocks for creating modular and efficient systems. They are used to construct lightweight yet durable frames for machines, workstations, and other support structures. For instance, in a factory setting, aluminium profiles can be assembled to form the framework for automated production lines, robotic workcells, and conveyor systems. The modular nature of aluminium extrusion profiles allows for easy customization and reconfiguration, adapting to changing production needs. Whether it's a small-scale electronics assembly line or a large automotive manufacturing facility, aluminium frames provide the necessary strength to support heavy equipment while being easy to install, dismantle, and relocate. This flexibility saves both time and money in industrial operations.
2. Conveyor Systems
T-slot aluminium profiles, in particular, have revolutionized conveyor systems in industries ranging from food processing to logistics. These profiles feature grooves or slots along their length, which allow for the easy attachment of accessories such as rollers, belts, and sensors without the need for welding or complex machining. This means that conveyor belts can be quickly assembled, modified, or extended based on the specific requirements of the production process. In a packaging plant, for example, a T-slot aluminium conveyor system can be customized to handle different package sizes and weights, with adjustable heights and speeds. The lightweight nature of aluminium also reduces the power consumption required to operate the conveyor, contributing to overall energy savings. Additionally, the smooth surface of aluminium profiles minimizes friction, ensuring smooth and reliable movement of products along the conveyor line, reducing the risk of jams and improving production efficiency.
E. Marine Industry
In the marine environment, where corrosion is a constant threat due to saltwater exposure, aluminium profiles have proven to be a reliable choice. They are used in the construction of boat hulls, decks, and railings. Aluminium boat hulls offer a combination of light weight and durability, allowing boats to move more efficiently through the water while withstanding the rigors of marine use. The material's resistance to corrosion means that boat owners spend less time and money on maintenance and repairs compared to boats made from other materials. Aluminium decks provide a non-slip surface and can be designed to drain water quickly, ensuring safety on board. Railings made from aluminium not only offer protection for passengers but also add to the aesthetic appeal of the vessel. Additionally, in marinas and docks, aluminium profiles are used for structural supports, gangways, and mooring posts. Their ability to resist the corrosive effects of saltwater and harsh weather conditions makes them ideal for these applications, providing long-term reliability and reducing the need for frequent replacements.
F. Aerospace Industry
In the highly demanding aerospace sector, every gram matters, and aluminium profiles have been a staple material for decades. Aircraft frames, both for commercial airliners and military jets, are constructed using high-strength aluminium alloys. These alloys offer an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, allowing the aircraft to carry more payload while consuming less fuel. Aluminium profiles are used to form the fuselage, wings, and tail sections, providing the structural integrity necessary for flight. Inside the aircraft, aluminium is also used for seat frames, overhead storage bins, and cabin partitions. Its lightweight nature helps in reducing the overall weight of the aircraft, contributing to fuel efficiency and lower operating costs. Moreover, aluminium's resistance to fatigue and its ability to withstand extreme temperature changes during flight make it a reliable choice in this critical industry. With ongoing research and development, new aluminium alloys and manufacturing techniques continue to enhance its performance and applicability in aerospace applications.
V. Conclusion
In conclusion, aluminium profiles, including standard and custom ones, have found extensive applications across various industries. From construction to aerospace, automotive to marine, their unique properties like lightweight, strength, and corrosion resistance make them indispensable. Understanding the differences between standard and custom profiles, along with key selection factors such as strength, size, and finish, is crucial for project success. Remember to collaborate with a reliable supplier. Now, here's an interesting question for you: If you were to design a futuristic transportation vehicle, how would you utilize aluminium profiles in innovative ways to enhance its performance and functionality?


 En
En



 Location:
Location:
















